Linux.osm
Ziel 1: osm-tile
Installation eines eigenen "Tile"-Servers. Also eines PNG-Kartenlieferanten über das HTTP-Protokoll. Es soll 100% kompatibel sein zu den bestehenden Tile-Servern des OpenStreetMap Projektes. In Zukunft soll dieses Projekt den Tile-Server-Part des kommerziellen xServer ersetzen.
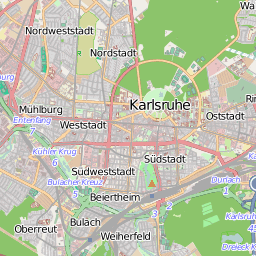
|
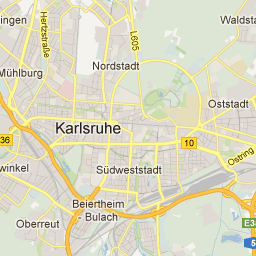
|
Das Bild zeigt ein einzelnes Tile (=Kachel) in der Zoom-Stufe 12, links von "openstreetmap", rechts von "google". Über einen typischen Tile-Server würde man diese Kachel über folgende URL erhalten:
- OpenStreetMap: http://tile.openstreetmap.org/12/2143/1406.png
- Google: http://mt0.google.com/vt/x=2143&y=1406&zoom=5
- Man beachte bei Google den invertierten zoom-Parameter, zoom=17-z
OrgaMon legt diese Kachel, je nach Provider, mit dem Dateinamen ~Provider~-12-2143-1406.png im Kartenpfad ab (im Moment sind die Provider "local-", "google-" und "osm-"), eine Kachel wird auf diese Art immer nur einmal angefragt.
Ziel 2: osm-geo
Installation eines eigenen "Geolokalisierungs"-Server. Als ein System das und Adressdaten (Text) in X,Y Geokoordinaten umsetzt. Realisierbar durch Nominatim.
OSM-Projekt Status
- Nov. 2012: Kontaktaufnahme zu geofabrik.de mit der Bitte um Hilfe http://www.geofabrik.de/
- 22.11.2012: ich will einen neuen Versuch starten mit http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/Application:/Geo/openSUSE_12.2/x86_64/
- 22.11.2012: setzte einen neuen Server auf ... Schritte bis osm2pgsl
- 23.11.2012: Dokumentation ...
Installation "Step by Step"
zunächst Ziel 1, Ziel 2 wird später integriert
Systemvoraussetzungen
- openSuSE 12.2 - 64 bit
- SSD mit 160 GByte freiem Platz vorzugsweise NICHT die System-Platte
- bei einfacher Datenhaltung (noch ohne Updates) reichen freie 80 GByte der System-Platte
- Dual-Core 3.0 GHz, 16 GByte RAM
- "zypper update", bis alle Updates eingespielt sind
Vorarbeiten
- Das Repository "Geo" von openSuSE integrieren
# # Repository Geo von openSuSE integrieren # zypper ar http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/Application:/Geo/openSUSE_12.2/ "Geo" # # Repository Cache neu erstellen, Trust-Anfrage mit "a" (=All) beantworten # zypper refresh
- Als Arbeitsverzeichnis wollen wir /srv/www/tile-server
md /srv/www/tile-server chmod 777 /srv/www/tile-server cd /srv/www/tile-server wget http://www.geofabrik.de/favicon.ico
Kartenbasis downloaden
Wir haben uns für einen Kartenausschnitt "ganz Deutschland" und ein "bischen Schweiz" entschieden. Als Grundlage laden wir jedoch ganz Europa herunter.
wget http://download.geofabrik.de/openstreetmap/europe.osm.pbf
|
Die genauen Download-Positionen werden noch nachgeliefert |
Wir wollen im "www.openstreetmap.de"-Style die Kacheln ausbelichten, also sind noch weitere Dateien notwendig
... für die Kueste
wget shoreline_300 wget processed_p
... fuer Ortsbezeichnungen und Landesgrenzen auf den sehr kleinen Zoomstufen
wget builtup_area wget 110m_admin_0_boundary_lines_land wget ne_10m_populated_places
... für den Karten-Style "Standard-OSM-Stil"
http://openstreetmap.de/germanstyle.html
Osmosis installieren
- Osmosis bneötigen wir, um aus Europa unseren Wunschbereich herausschneiden zu können, Infos gibt es hier http://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Osmosis
zypper install osmosis
Deutschland+Schweiz herauslösen
Eigentlich jetzt nicht direkt laut Landes-grenzen, sondern einfach ein viereckiger Bereich um dieses Gebiet. Die Koordinaten können hier http://www.dmap.co.uk/utmworld.htm abgeschätzt werden.
# # osmosis als Dienstleister für den "Kartenschnitt" nutzen # osmosis --read-pbf europe.osm.pbf --bb left=5.85 right=15.05 bottom=47.06 top=55.14 --write-pbf de_ch.osm.pbf # # Die erzeugte Datei dem User "postgres" sichtbar machen # mv de_ch.osm.pbf /var/lib/pgsql
- Es kommt "WARNING: Attention: Data being output lacks metadata. Please use omitmetadata=true" ich denke das kann ignoriert werden
PostgreSQL
Um Karten Rohdaten schneller abfragen zu können werden diese in eine PostgreSQL-Datenbank importiert. Dazu brauchen wir diesen Datenbank-Server.
zypper install postgresql postgresql-server postgresql-contrib postgresql-devel chkconfig --add postgresql rcpostgresql start
OPTIONAL: Datenbank auf einen "anderen" Pfad legen
in der Regel ist var/lib/pg/data (oder was auch immer das Standard-Verzeichnis für die GIS Datenbank ist) zu klein. Wir müssen sicherstellen, dass der "Tablespace" auf einem anderen Pfad läuft.
- sicherstellen, dass der Datenbank-Server aus ist:
rcpostgresql stop
- Die Ablage der Daten auf ein anderes Verzeichnis verbiegen
joe /etc/sysconfig/postgresql
- Folgende (oder Ähnliche) Änderung machen
# # POSTGRES_DATADIR="/srv/raid/osm/pg-data"
- Dienst nun starten
chkconfig --add postgresql rcpostgresql start
Postgresql: Tuning der Engine-Optionen
Frederik Ramm hat die PostgreSQL-Optimierung dokumentiert auf http://www.geofabrik.de/media/2012-09-08-osm2pgsql-performance.pdf
- Ich gehe hier mal vom Standard-Pfad aus:
joe /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf
# default ist 24MB shared_buffers = 8MB # default ist "auskommentiert" maintenance_work_mem = 4096MB # default ist "auskommentiert" fsync = off # default ist "auskommentiert" checkpoint_segments = 60 # default ist "auskommentiert" random_page_cost = 1.1 # default ist "auskommentiert" autovacuum = off
- Nicht vergessen den DB-Server neu zu starten
rcpostgresql restart
PostgreSQL: Lokale Zugriff regeln
joe /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf # # folgende Zeilen alle auf "trust" statt "ident" setzen: # local all all trust host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust host all all ::1/128 trust
- Nicht vergessen den DB-Server neu zu starten
rcpostgresql restart
Postgis2
zypper install postgis2
|
|
# # Unklar, ob folgendes notwendig ist: # su - postgis psql CREATE EXTENSION postgis; CREATE EXTENSION postgis_topology;
- Postgis2 liefert uns neue Datentypen für die SQL-Sprache von Postgresql (z.B. geometry)
# # mit folgender Abfrage # SELECT name, default_version, installed_version FROM pg_available_extensions WHERE name LIKE 'postgis%'; # # sollte man folgende Eregbnistabelle erhalten # | name | default_version | installed_version |------------------+-----------------+------------------- | postgis | 2.0.1 | | postgis_topology | 2.0.1 | |(2 rows) #
- Postgis2 liefert uns ein SQL-Skript, das die Datenbank-Struktur für eine leere Geo-Datenbank erstellt. Dort hinein fluten wir dann de_ch.
su - postgres createdb gis psql -d gis -f /usr/share/postgresql91/extension/postgis--2.0.1.sql psql gis alter role postgres with password 'postgres'; \q exit
osm2pgsql
Diese Programm flutet Kartendaten in eine vorbereitete Datenbank Struktur
zypper install osm2pgsql
# # Neuen Screen starten, da der folgende Import sehr lange dauert # screen # # Die Aktion im Benutzer-Account von postgres ausführen # su - postgres # Import starten # # osm2pgsql -c -C 8000 de_ch.osm.pbf
Mapnik
- Mapnik zeichnet aufgrund der Datenbankinhalte die Kacheln auf Anfrage
zypper install mapnik subversion
- Mapnik-Style mit Hilfsdateien installieren
mkdir -p /etc/mapnik/styles cd /etc/mapnik/styles svn export http://svn.openstreetmap.org/applications/rendering/mapnik osm cd /etc/mapnik/styles/osm mkdir world_boundaries cd world_boundaries wget http://tile.openstreetmap.org/world_boundaries-spherical.tgz wget http://tile.openstreetmap.org/processed_p.tar.bz2 wget http://tile.openstreetmap.org/shoreline_300.tar.bz2 wget http://www.naturalearthdata.com/http//www.naturalearthdata.com/download/10m/cultural/ne_10m_populated_places.zip wget http://www.naturalearthdata.com/http//www.naturalearthdata.com/download/110m/cultural/ne_110m_admin_0_boundary_lines_land.zip tar xjf processed_p.tar.bz2 tar xjf shoreline_300.tar.bz2 tar xzf world_boundaries-spherical.tgz unzip -d. ne_110m_admin_0_boundary_lines_land.zip unzip -d. ne_10m_populated_places.zip mv world_boundaries/* . rm -rf world_boundaries *bz2 *tgz *zip cd /etc/mapnik/styles/osm/ python generate_xml.py --dbname 'gis' --port 5432 --user 'postgres' --password 'postgres' --host 'localhost'
# # In der Datei inc/layer-shapefiles.xml.inc muss ein Vorkommen # von "110m_admin_0_boundary_lines_land.shp" mit einem vorangestellten "ne_" # ergaenzt werden (also auf "ne_110m_admin_0_boundary_lines_land.shp") - alternativ # das ausgepackte Shapefile umbenennen, Hauptsache beides passt zusammen. #
- Mapnik-Style testen
zypper in mapnik-python
cd /etc/mapnik/styles/osm joe generate_image.py # # die Zeile mit "bounds..." so anpassen, dass grosszügig unser Wunschbereich # sichtbar ist (Zeile 34) # bounds = (5, 46, 16, 56)
# # Jetzt rechnen lassen, dauert 5 min, danach liegt image.png im Verzeichnis # python generate_image.py # Nun sieht man, ob es irgendwelche Datenbankfehler oder sonstige Probleme # mit Shapefiles o.ae. gibt; anderenfalls wird nach ca. 5 Minuten (haengt von # der Groesse des gewaehlten Ausschnitts ab) ein image.png erzeugt, das man sich anschauen kann. #
tirex
tirex ist ein Dämon der auf Anfragen des mod_tile wartet, er zeichnet aber über mapnik
zypper install tirex
|
Die tirex-Installation funktioniert im Moment nicht (30.11.2012) |
mod_tile
liefert anhand von http-Requests Kacheln als png-Datei zurück
zypper install apache2-mod_tile
- mod_tile durch apache2 laden lassen
joe /etc/sysconfig/apache2 # # mod_tile aktivieren, indem man hinten den Kurznamen hinzumacht # apach2 ergänzt dies selbst durch mod_ # APACHE_MODULES="authz_host ... tile"
- mod_tile konfigurieren
Alle Einstellugen können wir über die Konfiguration des virtuellen Hosts steuern, siehe nächstes Kapitel
- http://svn.openstreetmap.org/applications/utils/mod_tile/readme.txt
- http://svn.openstreetmap.org/applications/utils/mod_tile/mod_tile.conf
Apache2, virtueller Host
- Grundsätzlich erst mal ermöglichen, dass es virtuelle Hosts geben kann
joe /etc/apache2/listen.conf # - name-based virtual hosting: # NameVirtualHost *:80
- Der bisherige Zugriff auf Apache2 (wenn dieser wieder funktionieren sollte) muss nun als virtueller Host "default" definiert werden
joe /etc/apache2/vhosts.d/00-default.conf <VirtualHost *:80> ServerName server.lummerland ServerAlias 192.168.115.38 server localhost DocumentRoot /srv/www/htdocs </VirtualHost>
- Den neuen virtuellen Host "tile" definieren
joe /etc/apache2/vhosts.d/tile.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName tile.server
DocumentRoot /srv/www/tile-server
# Arbeitsverzeichnis für mod_tile bestimmen
ModTileTileDir srv/www/tile-server
# You can either manually configure each tile set
# AddTileConfig /folder/ TileSetName
AddTileConfig / osm
# or load all the tile sets defined in the configuration file into this virtual host
# LoadTileConfigFile /etc/renderd.conf
# Timeout before giving up for a tile to be rendered
ModTileRequestTimeout 3
# Timeout before giving up for a tile to be rendered that is otherwise missing
ModTileMissingRequestTimeout 10
# If tile is out of date, don't re-render it if past this load threshold (users gets old tile)
ModTileMaxLoadOld 2
# If tile is missing, don't render it if past this load threshold (user gets 404 error)
ModTileMaxLoadMissing 5
# Socket where we connect to the rendering daemon
ModTileRenderdSocketName /var/lib/tirex/modtile.sock
# ModTileRenderdSocketName /var/run/renderd/renderd.sock
##
## Options controlling the cache proxy expiry headers. All values are in seconds.
##
## Caching is both important to reduce the load and bandwidth of the server, as
## well as reduce the load time for the user. The site loads fastest if tiles can be
## taken from the users browser cache and no round trip through the internet is needed.
## With minutely or hourly updates, however there is a trade-off between cacheability
## and freshness. As one can't predict the future, these are only heuristics, that
## need tuning.
## If there is a known update schedule such as only using weekly planet dumps to update the db,
## this can also be taken into account through the constant PLANET_INTERVAL in render_config.h
## but requires a recompile of mod_tile
## The values in this sample configuration are not the same as the defaults
## that apply if the config settings are left out. The defaults are more conservative
## and disable most of the heuristics.
##
## Caching is always a trade-off between being up to date and reducing server load or
## client side latency and bandwidth requirements. Under some conditions, like poor
## network conditions it might be more important to have good caching rather than the latest tiles.
## Therefor the following config options allow to set a special hostheader for which the caching
## behaviour is different to the normal heuristics
##
## The CacheExtended parameters overwrite all other caching parameters (including CacheDurationMax)
## for tiles being requested via the hostname CacheExtendedHostname
#ModTileCacheExtendedHostname cache.tile.openstreetmap.org
#ModTileCacheExtendedDuration 2592000
# Upper bound on the length a tile will be set cacheable, which takes
# precedence over other settings of cacheing
ModTileCacheDurationMax 604800
# Sets the time tiles can be cached for that are known to by outdated and have been
# sent to renderd to be rerendered. This should be set to a value corresponding
# roughly to how long it will take renderd to get through its queue. There is an additional
# fuzz factor on top of this to not have all tiles expire at the same time
ModTileCacheDurationDirty 900
# Specify the minimum time mod_tile will set the cache expiry to for fresh tiles. There
# is an additional fuzz factor of between 0 and 3 hours on top of this.
ModTileCacheDurationMinimum 10800
# Lower zoom levels are less likely to change noticeable, so these could be cached for longer
# without users noticing much.
# The heuristic offers three levels of zoom, Low, Medium and High, for which different minimum
# cacheing times can be specified.
#Specify the zoom level below which Medium starts and the time in seconds for which they can be cached
ModTileCacheDurationMediumZoom 13 86400
#Specify the zoom level below which Low starts and the time in seconds for which they can be cached
ModTileCacheDurationLowZoom 9 518400
# A further heuristic to determine cacheing times is when was the last time a tile has changed.
# If it hasn't changed for a while, it is less likely to change in the immediate future, so the
# tiles can be cached for longer.
# For example, if the factor is 0.20 and the tile hasn't changed in the last 5 days, it can be cached
# for up to one day without having to re-validate.
ModTileCacheLastModifiedFactor 0.20
## Tile Throttling
## Tile scrappers can often download large numbers of tiles and overly staining tileserver resources
## mod_tile therefore offers the ability to automatically throttle requests from ip addresses that have
## requested a lot of tiles.
## The mechanism uses a token bucket approach to shape traffic. I.e. there is an initial pool of n tiles
## per ip that can be requested arbitrarily fast. After that this pool gets filled up at a constant rate
## The algorithm has to metrics. One based on overall tiles served to an ip address and a second one based on
## the number of requests to renderd / tirex to render a new tile.
## Overall enable or disable tile throttling
ModTileEnableTileThrottling Off
## Parameters (poolsize in tiles and topup rate in tiles per second) for throttling tile serving.
ModTileThrottlingTiles 10000 1
## Parameters (poolsize in tiles and topup rate in tiles per second) for throttling render requests.
ModTileThrottlingRenders 128 0.2
###
###
# increase the log level for more detailed information
LogLevel debug
</VirtualHost>
<Directory "/srv/www/tile-server">
# AllowOverride None
# Options +ExecCGI -Includes
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
- Apache neu starten
rcapache2 restart
wget http://tile.server/12/2143/1406.png
Update
- Im Moment dokumentiere ich hier nur den Zeitaufwand/Volumenbedarf für ein Update.
| Schritt | Dauer [Min] |
Neues Volumen [GiByte] |
Zuvor freigebbares Volumen [GiByte] |
Bedarfsspitze [GiByte] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Download von Europa | 90 | 9 | 9 | |
| Herausschneiden von de+ch | 17 | 2,2 | 11,2 | |
| Import in die Datenbank | 59 | 27 | 11,2 | 27 |
weiterführende Quellen
Allgemeine Quellen
- http://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/OnDemandTileServer
- http://gis.hsr.ch/wiki/HowTo_OpenStreetMap
- http://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Osmosis
- http://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Howto_real_time_tiles_rendering_with_mapnik_and_mod_python
- http://mapserver.org/introduction.html#introduction
- http://trac.mapnik.org/wiki/MapnikCodeSprint/MCS01/Results
- http://www.mapnik.org/
- http://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Osm2pgsql
- http://tilecache.org/
- http://postgis.refractions.net/
- http://trac.osgeo.org/postgis/wiki/UsersWikiPostgreSQLPostGIS
- http://trac.osgeo.org/postgis/wiki/UsersWikiPostGIS20Ubuntu1110src
- http://www.kelvinism.com/howtos/revised-mod_tile-howto/
Download-Quellen
# die ganze Welt wget http://planet.openstreetmap.org/planet-latest.osm.bz2 # nur Deutschland wget http://download.geofabrik.de/openstreetmap/europe/germany.osm.bz2
# Zusätzliche Dateien wget http://tile.openstreetmap.org/world_boundaries-spherical.tgz wget http://tile.openstreetmap.org/processed_p.tar.bz2 wget http://tile.openstreetmap.org/shoreline_300.tar.bz2 wget http://www.naturalearthdata.com/http//www.naturalearthdata.com/download/10m/cultural/10m-populated-places.zip wget http://www.naturalearthdata.com/http//www.naturalearthdata.com/download/110m/cultural/110m-admin-0-boundary-lines.zip wget http://trac.openstreetmap.org/browser/applications/utils/export/osm2pgsql/900913.sql?format=raw -O 900913.sql
Source-Code OrgaMon
- Delphi OpenSource (Umrechnung X,Y in TileName) http://orgamon.de/websvn/filedetails.php?repname=OrgaMon&path=%2FPASconTools%2FOpenStreetMap.pas